A Bank without a Branch
Ever heard about a bank operating in India without a branch. Here is one such story of digital India bringing basic banking facility to the bottom of the pyramid.
As a guest faculty I have been taking sessions on digital payment system for one of the B-Schools. In one of the sessions, I asked my students what is being truly digital all about in terms of payment and banking and one of the students replied – “May be a bank which doesn't have a branch”. So, I asked them do you know of bank which does not have a branch and gave them a task to identify a bank which does not have a branch. Whether such bank exists or not, we will come to this later but this whole discussion is related to an important concept in banking called Payment Banks.
Now first let me deep dive into what are payment banks how different they are from the normal banks may see and why did we need payment banks. Banking is one of the key needs for the population and even in banking ability to do payments and transaction is considered the very basic primary need which 100% of the population should have. The government and regulator have been trying multiple strategies to bring everybody into the banking system in India however still by 2014, half of the India was still not part of the banking system.
This is where the regulator felt a need to have a special kind of bank which is focused on the bottom of the pyramid to cater to the basic needs of banking system which is making payments and transactions. Also, this bank had to be different than traditional public and private sector banks so that it can serve the bottom of the pyramid which the traditional banks have not been able to do. This led to the creation of policy document on payment banks, and this is how the concept of payment banks emerged from RBI granted in-principal approval to eleven players to launch payment banks. 3 players subsequently withdrew application. Of the remaining 8, 7 commenced operations/
FINO payment bank was one of the payment bank licenses. Have you seen any branch for FINO payment bank? If no, then why? You would like to watch this video to get an answer about why FINO payment bank doesn't have a branch.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oF4_RbBNhTw
Sounds interesting are truly digital company built on a digital stack without a Capex model without heavy physical assets and physical branches. Want to understand the business model in detail wearing and investing hat. Let us go ahead and try to understand what FINO business model all is about.
FINO Payment Bank operates in a unique niche, catering to the middle-income segment in rural and semi-urban areas of India, providing essential banking services through a vast network of merchants. FINO Payment Bank is a payment bank, operating in India's emerging market segment. As a payment bank, it provides various banking and payment services without offering lending facilities (not allowed by regulator for Payment banks and hence, its financial statement structure is different from a typical lending bank). Instead, it partners with other banks and financial institutions to cater to the financial needs of its customers. This model allows FINO to serve unbanked or underserved populations, providing them with easy access to essential banking services. However, FINO is allowed to provide deposit services and other banking facilities with certain restrictions, and it charges either a subscription fee or a transaction fee on those banking facilities and makes money.
Let us understand what are the various rules and regulations under which a Payment Bank operates.
As the commercial banks, the payment banks will also accept the money of the people as a deposit, but the limit is fixed, which means the payments banks can accept deposits up to a maximum of Rs. 1 lakh from a customer.
Payments banks must use the word "Payments Bank" in their names to look different from other banks.
Payments banks will be entitled to issue ATM or debit cards to their customers but cannot issue a credit card.
Payments banks will be authorized to open both savings and current accounts of their customers but cannot provide loans or lending services to customers.
Payments banks cannot accept deposits from the Non-Resident Indians (NRIs).
Payments banks will be allowed to make personal payment & receive cross border remittance on current account.
Payments banks will have to deposit the amount in the form of a Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) with RBI as other commercial banks do.
Payments Banks will have to invest a minimum of 75% of its demand deposits in government treasury/securities bills with maturity up to one year and hold a maximum of 25% in currents and fixed deposits with other commercial banks for operational purposes.
Payment banks can provide the facility of utility bill payments, internet and mobile banking to its customers and the public.
Payments banks cannot open subsidiaries to undertake Non-Banking Financial Services activities.
Payments bank with approval from RBI, can work as a partner with other commercial banks and can sell mutual funds, pension products, and insurance products.
Payments banks can become a business representative of any other bank, but it will have to comply with the guidelines of the Reserve Bank of India.
FINO Payment Bank's Business Model:
FINO Payment Bank operates through a vast network of merchants, primarily small Kirana stores, in rural and semi-urban areas. These merchants act as intermediaries, providing banking services to customers who may not have access to traditional banks. The process is facilitated through dedicated apps for merchants and customers. This unique merchant-based model allows FINO to bridge the gap between customers and banking services effectively.
Product Offerings:
FINO Payment Bank offers a range of financial products and services, both physical and digital. The physical ecosystem includes micro-ATMs, Aadhaar-enabled money withdrawals, and cash management services for various financial institutions. The digital ecosystem encompasses online payments, deposits, loans, mutual funds, and insurance products. This diverse bouquet of services ensures that customers have access to a wide range of financial solutions.
Revenue Model:
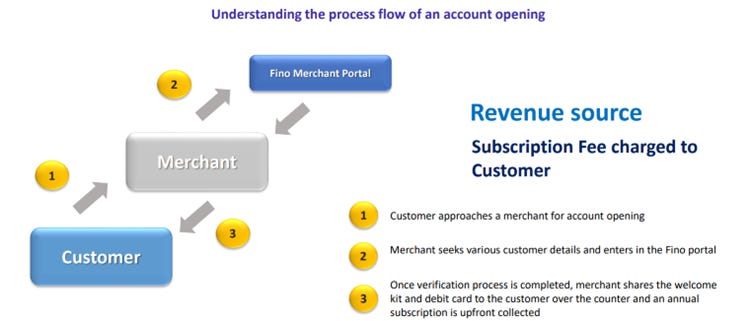
FINO Payment Bank's revenue model is based on a mix of transaction-based and subscription-based fees. While some services involve transaction charges, others, such as opening deposit or CASA accounts, require an annual subscription fee. This revenue structure ensures that the company generates sustainable income from its offerings.
Continuing our analysis of FINO Payment Bank, we will delve into its core product offerings and revenue model. FINO Payment Bank provides essential banking services, including remittance, micro-ATMs, cash management, third-party cross-sell, and basic banking through its unique merchant-based model. Additionally, we will discuss the concept of throughput and take rate, crucial metrics for understanding the company's revenue generation. Let's explore these offerings in detail.
Understanding Key Metrics: Throughput and Take Rate
To analyze FINO Payment Bank's revenue model further, we need to understand two essential metrics: throughput and take rate.
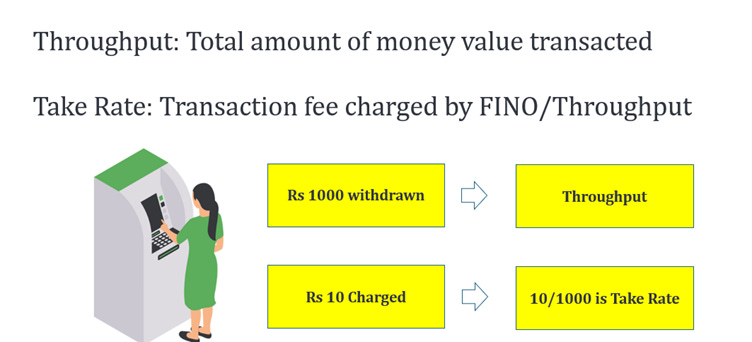
Throughput: The term throughput refers to the total value of money being transacted by customers through FINO's services. It represents the sum of all transactions processed by the bank.
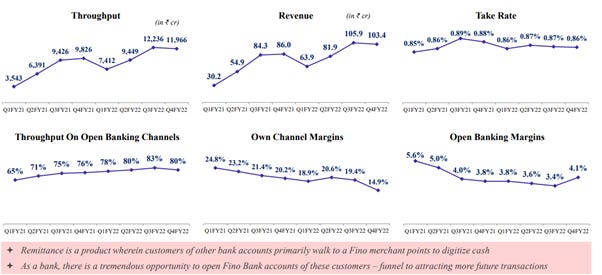
Take Rate: The take rate is the fee charged by FINO Payment Bank on each transaction as a percentage of the total throughput. For instance, if the take rate is 0.86% on a throughput of ₹12,000 crore, FINO would earn around ₹105 crore in revenue.
Remittance:
Remittance is one of the oldest products offered by FINO Payment Bank, allowing customers to transfer money to beneficiaries. When a customer wants to remit money, they approach a nearby merchant who already has an account with FINO. The merchant assists the customer in transferring the money to the beneficiary's account.
FINO charges a percentage-based transaction fee from the customer, and a part of this fee goes to the merchant as an incentive. This remittance service is facilitated through FINO's own API or other open API channels. Although the remittance throughput has experienced some fluctuations due to external factors like migration during the pandemic, FINO has been able to maintain a steady revenue stream from this product. Also, FINO usages remittance, Micro-ATM and AEPS as hook strategy to connect with customer and offer sticky high growth high margin services in the form of CASA.
Micro ATM and AEPS (Aadhaar Electronic Payment System):
FINO Payment Bank's micro-ATMs and AEPS services provide a cost-effective alternative to traditional ATMs in rural areas, where ATMs are less accessible. Merchants acting as "bankers" enable customers to withdraw cash and perform other banking transactions.
FINO earns revenue through subscription fees and transaction fees from these services. Also, FINO usages remittance, Micro-ATM and AEPS as hook strategy to connect with customer and offer sticky high growth high margin services in the form of CASA.
CASA (Current Account and Savings Account):
FINO offers basic banking services, such as current accounts and savings accounts, to its customers through debit cards and online platforms.
CASA has been a game changer for FINO being a high growth high margin product. Also, CASA is going through the exponential growth curve due to high growth rate in addition of new subscribers and renewal of subscription from old subscribers leading to an exponential growth rate in revenue contribution. These accounts are subscription-based, providing a steady source of revenue for the bank.
The below table provides more details on the growth journey of CASA due to high new subscriber growth and decent renewal rates. Higher renewal rate, higher CASA average balance and higher debit card spends works to the benefit of FINO leading to higher customer stickiness.
Below chart highlights how strongly CASA has driven overall revenue where its share has gone from 12% to 18% last year and last quarter, it was 20% of revenue share.
Cash Management Facility:
The cash management facility is more of a business-to-business (B2B) service, where FINO manages cash for various industries, including e-commerce and NBFCs. This service is not related to customers but contributes to FINO's revenue generation and also a high margin business. In terms of business vertical attract.
Third-Party Cross-Sell:
FINO Payment Bank offers a range of financial products from partner institutions, including insurance companies and other financial institutes. These third-party products are cross sold to customers through FINO's platform, creating an additional revenue stream for the company. As FINO transitions into its digital journey, for coming years, this is going to be an important segment.
Another key thing to note is that merchant stays at the centre to grow the subscriber base and offer these various products. FINO has shown a very respectable growth so far in driving its merchant network with last year growth at 34%
Now, let me tell you that officially FINO payment bank does have 61 branches as per website data dated June 2020 (https://www.finobank.com/uploads/content/fpb-branches-22nd-june-2020.pdf), however, they are able to serve lakhs of customers through 13 Lakh+ merchants and in some way, every merchant store is a branch in spirit. These 60+ branches kind of act as key branch centers. In total, FINO operates through 724671 banking outlets, 61 bank branches and 130 customer touch points. However, for the kind of scale they have built using their unique business model, it is very different from a regular bank and the purpose of title of this article is to capture the spirit and essence of business model.
In summary, FINO has multiple revenue streams and a dynamic mix of products, some of which are high-growth and high-margin businesses and some are pure hook products. The key metrics to track are the take rate, client count, throughput per client, and throughput per transaction. The company's growth is driven by high subscription growth rate client growth rates and increasing throughput metrics.
Below table highlights the importance of cash management system along with CASA in terms of its importance for FINO to drive both growth as well as profitability
Risks:
New and Unproven Business: FINO is a new player in the payment banking industry, and its business model is still unproven. This uncertainty poses a significant risk as there might be unforeseen challenges in scaling and sustaining the business.
Competitive Threats: Established players like Airtel and Jio also hold payment bank licenses, and they have a vast customer base and resources. They can potentially enter the market aggressively and pose a threat to FINO market share.
Declining Remittance Market: The remittance market, which is one of FINO major revenue sources, might face challenges in the future due to factors like increasing digital literacy, reducing the need for traditional remittance services.
Cash Handling Risks: Being a cash-driven business, FINO faces risks related to fraud, security, and operational issues associated with cash handling. Any significant security breaches or fraud could harm the company's reputation.
What is there for future:
After showing a significant performance for last few years from a loss making company to almost Rs 70-75 Crore profit on current quarterly revenue run rate, now, FINO has set its strategic goals for FY26 under FINO 2.0
Time would tell if FINO will be able to achieve it or not, however, given the regulatory constraints and competitive landscape, FINO has done a commendable job not only to drive profit for its investors but also to bring financial inclusion and basic banking facilities to the unserved population of India, the key reason why Payment banks came into existence.
Want to be a part of our journey and analyze more such interesting businesses with us at the right time? Explore below link
Annual Membership | Scientific Investing -Technofunda Algorithmic Trading